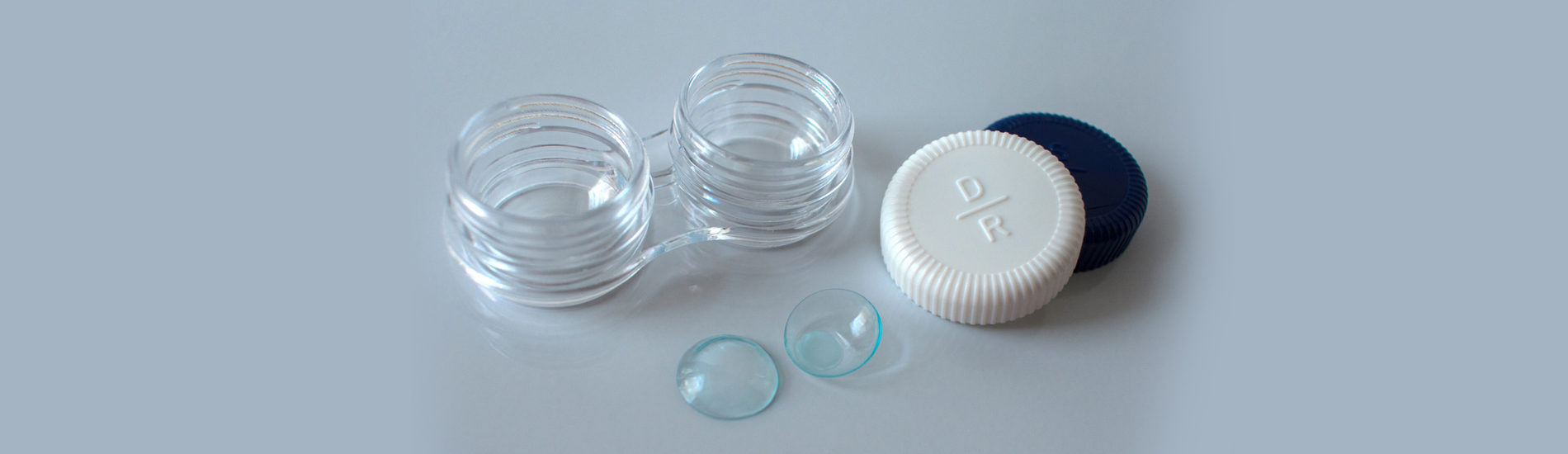
Contact Lenses
Contact lenses, like eyeglasses or LASIK surgery, can correct your nearsightedness, farsightedness and astigmatism. Among Americans who need vision correction, about 20 percent wear contact lenses.
While some people enjoy making a fashion statement with eyeglasses, others prefer their appearance without them. Contact lenses can achieve this without irreversible surgery. Contact lenses can also provide a full field of unobstructed vision, which is great for sports.
Contact lenses have been around for more than a hundred years. During that time, many advancements have allowed just about everyone to wear contactlenses. If you were told in the past that you couldn't wear contact lenses, odds are that's not true today. There are more convenient and healthy contact lens options than ever.
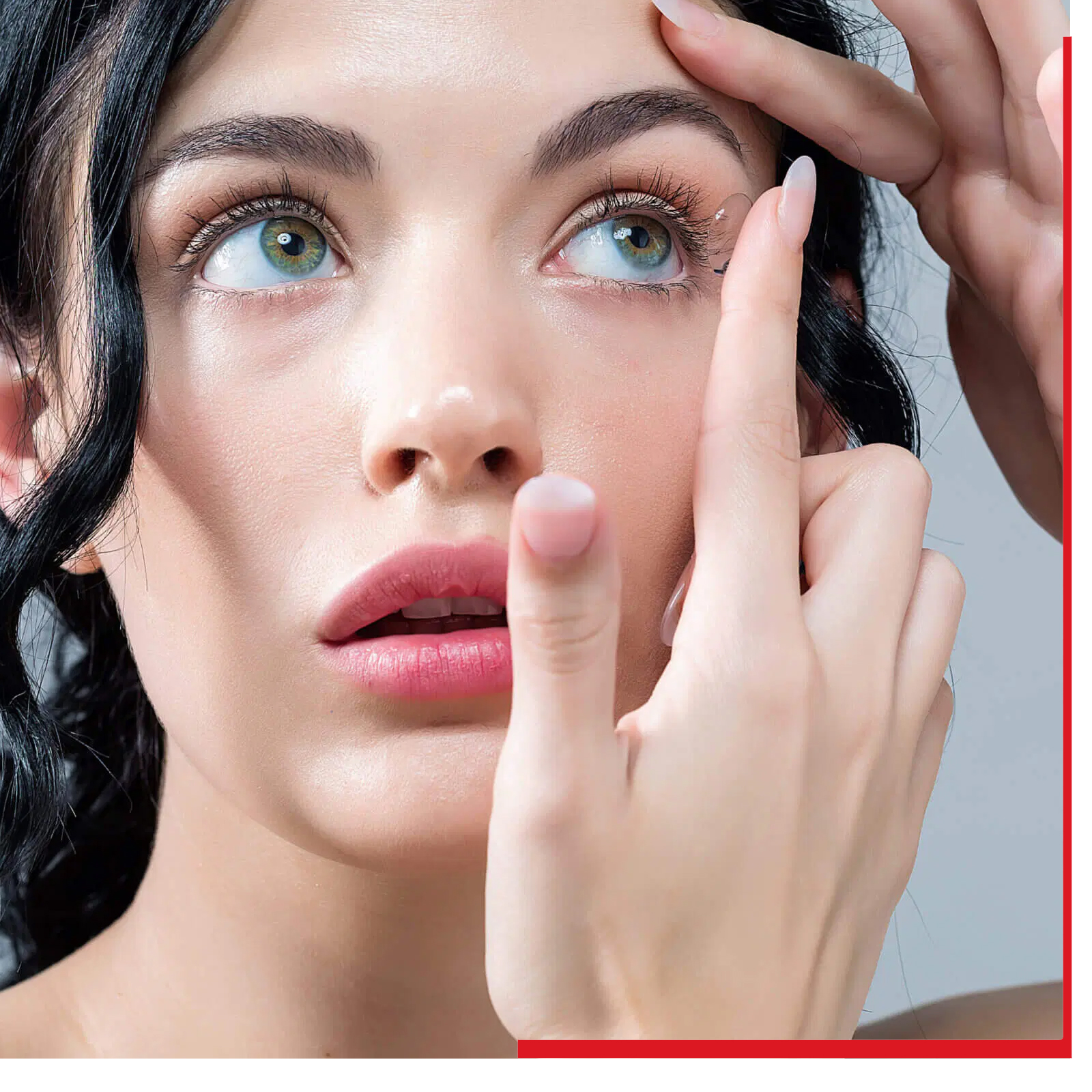
If you're new to contact lenses, your first step is to see an eye doctor. In the United States, contact lenses are a prescription item, just like pharmaceuticals. They must be prescribed and properly fitted by an eye care professional (ECP). Your ECP will evaluate your visual needs, your eye structure, and your tears to help determine the best type of lens for you.
The many types of contact lenses currently available can be grouped in various ways according to :
- What they're made of
- How long you wear them without removal
- How often you dispose of them
- The design of the lens
- Contact lens materials
- Contact lens wearing time
- Various designs
- Color, special-effect, UV-inhibiting lenses, etc.
- How to decide which lens is right for you
- Wear and care
- If you have a problem with contacts
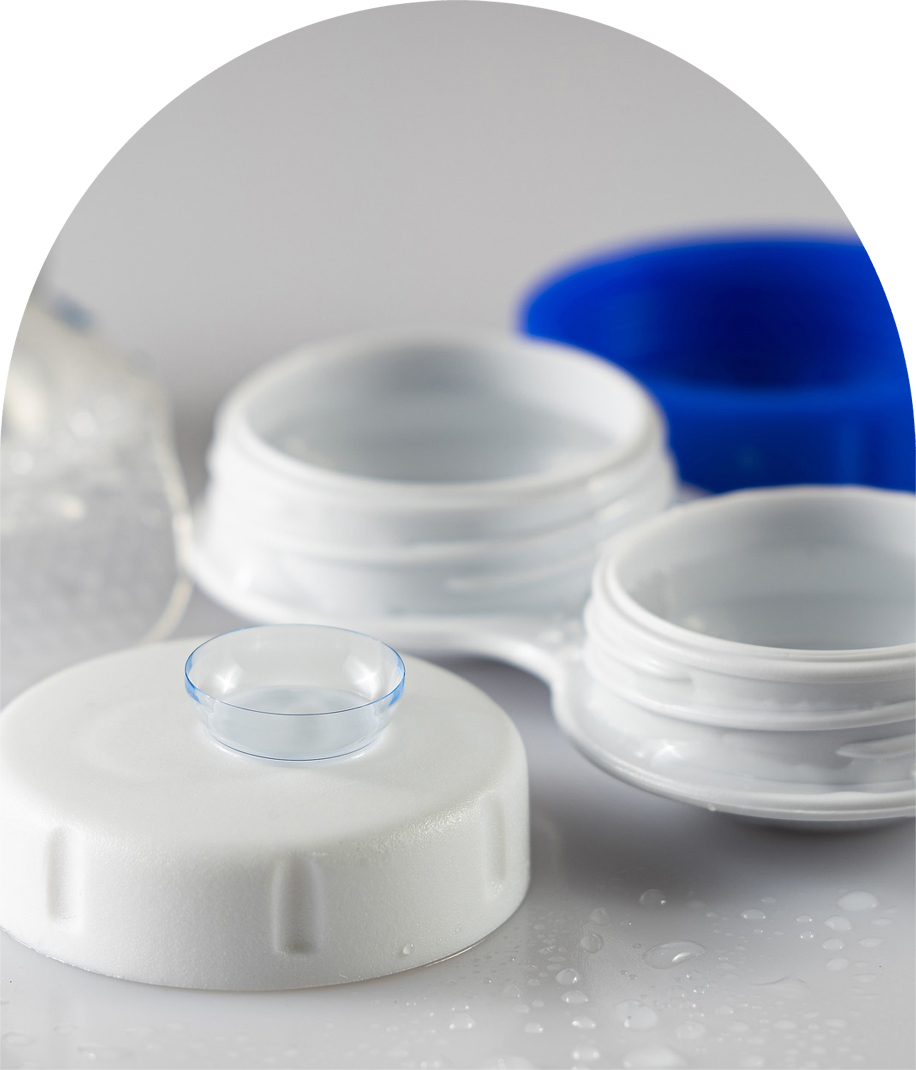


CONTACT LENS MATERIALS
Contact lenses are made from the following materials:
Hard lenses are made of Plexiglas or Lucite (PMMA). These lenses are virtually obsolete and rarely used.
Rigid glass permeable (RGP) contact lenses are made from rigid, waterless plastics and are good for individuals with presbyopia or a high astigmatism. These lenses are usually about 8 millimeters in diameter, which is smaller than your iris.
Silicone hydrogel contact lenses are the newest material to be used, and has recently replaced lenses made from hydrogel plastics.
Silicone hydrogel has become the contact lens of choice for many eye care practitioners, because they allow more oxygen to pass through the lens to the eye and are less prone to dehydration.
CONTACT LENS WEAR
Refers to how long you can wear your contact lenses for before removal. Due to advances in research in eyewear, two types of lenses can be classified based on wear time, and they are as follows:
Daily Wear These lenses can only be worn in the daytime, and need to be removed at night.
Extended Wear These lenses are safe to be worn for two or more days and nights.

CONTACT LENS REPLACEMENT
Disposable contact lenses can be prescribed for daily wear or extended wear, and most commonly fall into one of these replacement categories:
Disposable lenses
These lenses need to be replaced every two weeks or earlier.
Frequent replacement lenses
These lenses need to be replaced every thirty days or quarterly.
Traditional (reusable) lenses
These lenses need to be replaced every six months or longer.
CONTACT LENS DESIGNS
Thanks to the ever-changing world of fashion, there are many types of contact lens designs available to correct vision problems. These are four of the most common types:
Spherical Contact Lenses
These lenses are the typical rounded design of contact lenses, which can correct myopia (nearsightedness) and hyperopia (farsightedness).
Bifocal Contact Lenses
These lenses contact different zones for near and farsighted vision to correct presbyopia, the age-related decrease in ability to obtain a full range of vision.
Orthokeratology Lenses
These lenses are specially designed to reshape the cornea during sleep, providing lens-free daytime wear.
Toric Contact Lenses
These lenses provide correction for astigmatism, myopia and hyperopia.
All of these lenses can be custom made for hard-to-fit eyes. Many other additional lens designs are available. They are usually less common and fabricated for use in special situations, such as correcting keratoconus.
Additional Contact Lens Features include the following:
Coloured Lenses
Many of the types of lenses described above also come in colours that can enhance the natural colour of your eyes – to make green eyes appear greener, for instance. Other lenses can be made to change your natural eye colour completely.
Special Effects Lenses
Novelty, costume or theatrical lenses take colouration one step further to make your eyes look like that of a cat, zombie, or provide another type of unique effect.
Prosthetic Lenses
Coloured contact lenses can also be used for medical purposes. People that have incurred eye damage because of an accident or illness can use a custom, opaque coloured lens to make their eye appear normal by matching the lens to the appearance of their original eye.
Custom Lenses
A customized lens might be useful for some individuals when conventional lenses are not working, as they would expect to.
UV-Inhibiting Lenses
Today, many contacts incorporate an ultraviolet blocker in the lens material, which cuts down on UV light that may cause cataracts or other eye issues. It provides some protection, but does not cover the entire eye. As a result, it does not substitute for traditional sun protection like good quality sunglasses.
Hybrid Lenses
One brand of lens features a GP centre with a soft, outer skirt, providing wearers with both the crisp optics of a rigid lens, and the comfort of a larger, soft lens.

